The BETWEEN Operator is useful because of the SQL Query Optimizer. Although BETWEEN is functionally the same as: x <= element <= y, the SQL Query Optimizer will recognize this command faster, and has optimized code for running it.
This operator is used in a WHERE clause or in a GROUP BY HAVING clause.
Rows are selected that have a value greater than the minimum value and less than the maximum value.
It’s important to keep in mind that the values entered in the command are excluded from the result. We get just what is between them.
Here is the syntax for using the function in a WHERE Clause:
select field1, testField
from table1
where testField between min and max
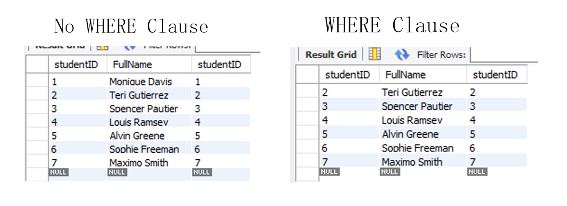
Here is an example using the student table and the WHERE clause:
-- no WHERE clause
select studentID, FullName, studentID
from student;
-- WHERE clause with between
select studentID, FullName, studentID
from student
where studentID between 2 and 7;
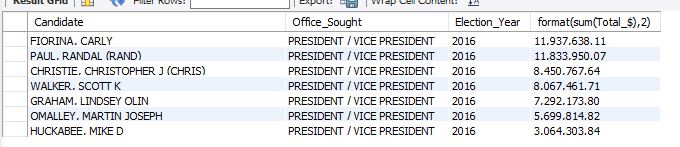
Here is an example using the campaign funds table and the having clause. This will return rows where the sum of the donations for a candidate are between $3 Million and $18 Million based on the HAVING clause in the GROUP BY part of the statement. More on aggregation in that guide.
select Candidate, Office_Sought, Election_Year, format(sum(Total_$),2)
from combined_party_data
where Election_Year = 2016
group by Candidate, Office_Sought, Election_Year
having sum(Total_$) between 3000000 and 18000000
order by sum(Total_$) desc;